Scabies

Scabies is a highly contagious skin infestation caused by the microscopic mite Sarcoptes scabiei. It is characterized by intense itching and a rash with small, red bumps or blisters. Effective treatment is essential to eliminate the mites, relieve symptoms, and prevent the spread of the infestation. Here’s a guide to scabies treatment:
1. Consult a Healthcare Provider:
If you suspect you have scabies or have been in close contact with someone who has it, consult a healthcare provider. They can confirm the diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment.
2. Prescription Medications:
The most common treatment for scabies involves the use of prescription medications applied to the skin. Common options include:
Permethrin Cream: This is the most commonly prescribed treatment. It is a topical cream that is applied to the entire body from the neck down, left on for several hours, and then washed off. It kills the mites and their eggs.
Understanding, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Indirect Contact: Scabies mites can survive for a short period away from the human body, so transmission can occur through contact with infested clothing, bedding, or towels.
- Crowded Environments: Scabies outbreaks are more common in crowded or close-quarters settings, such as nursing homes, dormitories, and prisons.
- Symptoms: The primary symptom of scabies is itching, which can be severe and often worsens at night. Other common symptoms include:
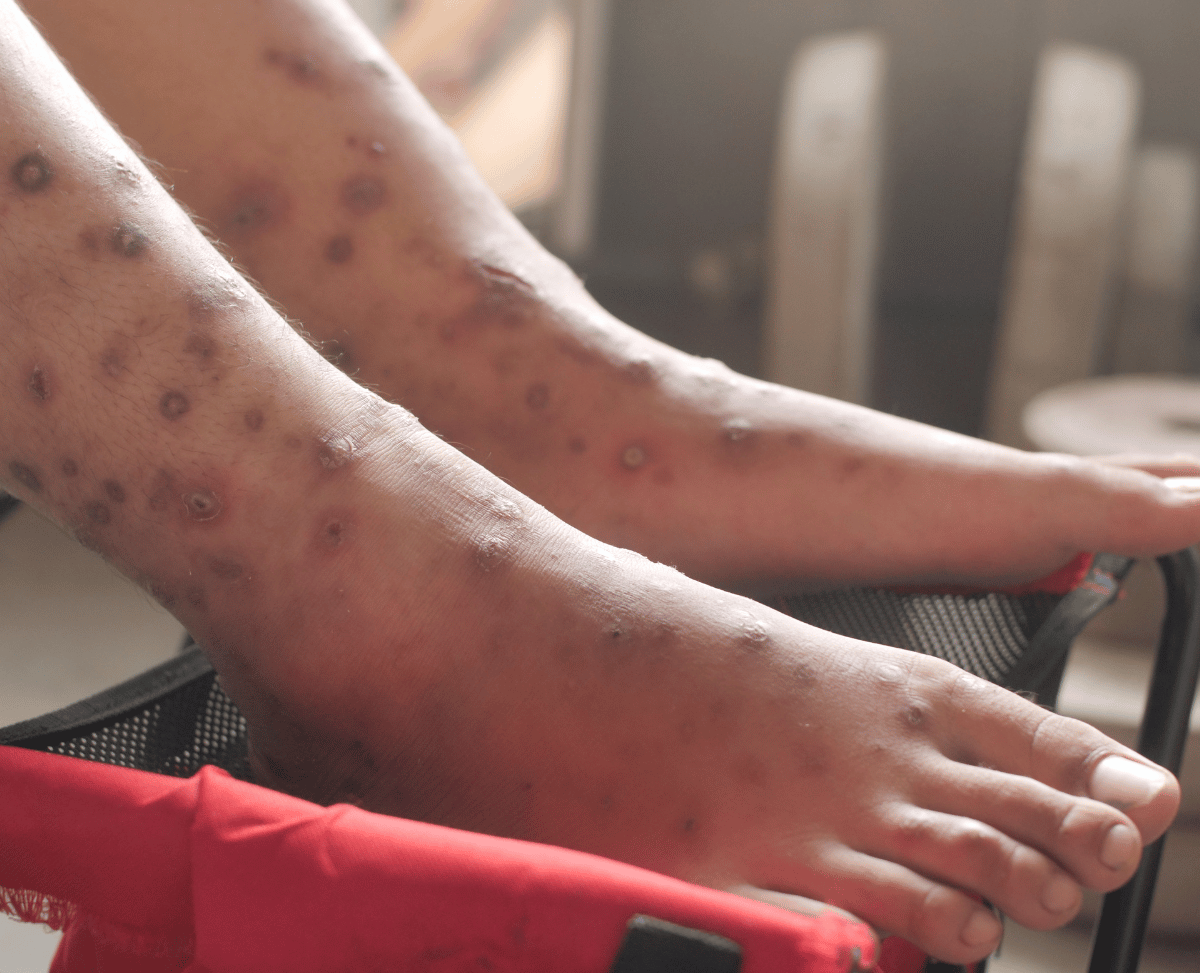
Scabies is a contagious skin condition caused by a tiny mite known as Sarcoptes scabiei. It is characterized by intense itching and a rash. Scabies is highly contagious and can be transmitted through close physical contact. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for scabies.
Causes and Transmission:
Scabies is caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. The female mites burrow into the outer layer of the skin, where they lay eggs, leading to an infestation. Scabies is highly contagious and can spread through:
Rash: Scabies typically causes a red, bumpy rash with small, raised blisters or pustules. The rash can appear in various areas of the body but is most common in the folds of the skin, such as between the fingers, on the wrists, elbows, armpits, waist, buttocks, and genitals.
Burrows: Tiny, raised, grayish-white or flesh-colored lines may be visible on the skin’s surface. These are the burrows created by the mites.
Secondary Infections: Scratching the itchy rash can lead to open sores, which can become infected with bacteria.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing scabies often involves a healthcare provider examining the affected skin and identifying characteristic signs like burrows, rashes, and the distribution of the lesions. In some cases, a skin scraping may be taken and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of mites, eggs, or feces.
Treatment: Scabies is treatable, and treatment typically involves the use of scabicide medications. Common treatment options include:
Topical Scabicides: These are prescription or over-the-counter creams or lotions that contain permethrin or ivermectin. They should be applied to the entire body, including the neck down, and left on for a specified duration before washing off.
Scabies is a contagious skin condition caused by a mite infestation that results in intense itching and a characteristic rash. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential to prevent the spread of scabies. If you suspect you have scabies, or if you have been in close contact with an infected person, seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment. Additionally, it’s crucial to follow preventive measures to avoid transmission to others.
